Version: 5.2.1
Least Squares: fitting a line to a sequence of 2d-points
Danny Yoo <dyoo@hashcollision.org>
This is a simple implementation of the least squares method for lines,
described in a standard statistics textbook [larsen2006]. Given a sequence of
2d-points, this library computes the slope and intersect of a line
that best fits those points.
Here’s a quick-and-dirty example that shows how to use this package with
a tool like Racket’s
plot graph-plotting libraries:
| > (require (planet dyoo/least-squares)) |
|
| > (define data '(#(2.745 2.08) #(2.7 2.045) #(2.69 2.05) | | #(2.68 2.005) #(2.675 2.035) #(2.67 2.035) | | #(2.665 2.02) #(2.66 2.005) #(2.655 2.01) | | #(2.655 2.0) #(2.65 2.0) #(2.65 2.005) | | #(2.645 2.015) #(2.635 1.99) #(2.63 1.99) | | #(2.625 1.995) #(2.625 1.985) #(2.62 1.97) | | #(2.615 1.985) #(2.615 1.99) #(2.615 1.995) | | #(2.61 1.99) #(2.59 1.975) #(2.59 1.995) | | #(2.565 1.955))) |
|
|
| > (require plot) |
|
|
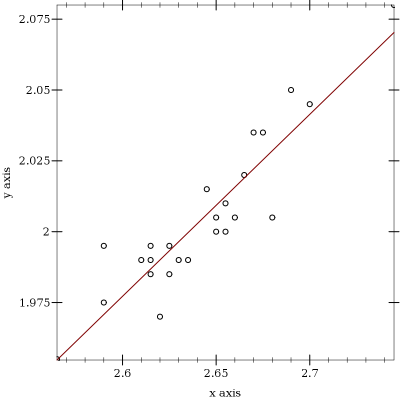
|
One of the more direct ways to use the library is to get the slope and intersect
with
least-squares:
| > (define-values (a-slope an-intersect) | | (least-squares '((0 -0.2342) (1 1.0001) (2 1.82123) (3 3.1415926)))) |
|
|
| > a-slope |
1.0948507800000002 |
| > an-intersect |
-0.2100955200000003 |
|
|
| > (my-linear-function 1) |
0.8847552599999999 |
| > (my-linear-function 2) |
1.9796060400000002 |
| > (my-linear-function 314) |
343.5730494000001 |
1 API
|
| | data | | : | | | (sequenceof (or/c (sequence number number) | | posn)) |
|
|
Computes the slope and intersect for a line that best
fits the points according to the method of least squares and returns
them as two values.
For example:
| > (define-values (a-slope an-intersect) | | (least-squares '((2.718 3.1415926) (1.618 1.414213)))) |
|
|
| > a-slope |
1.5703450909090884 |
| > an-intersect |
-1.1266053570909036 |
Constructs a function that fits the given data.
For example:
|
|
| > (g 0) |
-1.1266053570909036 |
| > (g 3) |
3.584429915636362 |
| > (g 27) |
41.27271209745448 |
Example:
Bibliography
| [larsen2006] | | Richard J. Larsen and Morris L. Marx, An Introduction to Mathematical Statistics and Its Applications, 4th Edition. 2006. |
