Animated Canvas
M. Douglas Williams <doug@cognidrome.org>
This library provides an animated-canvas% class that specializes the GRacket canvas% class to provide a simple double-buffered animation capability. Simple demonstration programs are also provided, including two that show how to animate plots using the new plot collection.
Everything in this library is exported by a single module:
| (require (planet williams/animated-canvas/animated-canvas)) |
1 Theory of Operation
This section assumes you are familiar with the canvas% class.
An animated canvas uses two bitmaps to provide a double-buffered animation capability. This is implemented by a new class animated-canvas% that specializes the canvas% class. At any specific time, one bitmap, the background bitmap, is being used for all drawing operations and the other bitmap, the foreground bitmap, is being used to paint the canvas.
The swap-bitmaps method is used to swap the background and foreground bitmaps. When the bitmaps are swapped, the contents of the new foreground bitmap —
The device context returned by the animated canvases’s get-dc method is the device context of the background bitmap. This value is not valid across calls to swap-bitmaps. Therefore, it is important to re-retrieve, via get-dc, the device context across bitmap swaps.
The animated canvas also supports resizing on the canvas, which automatically resizes the background buffer after the bitmaps are swapped.
2 Interface
constructor
(new animated-canvas% [parent parent] [ [style style] [paint-callback paint-callback] [label label] [gl-config gl-config] [enabled enabled] [vert-margin vert-margin] [horiz-margin horiz-margin] [min-width min-width] [min-height min-height] [stretchable-width stretchable-width] [stretchable-height stretchable-height]]) → (is-a?/c animated-canvas%)
parent :
(or/c (is-a?/c frame%) (is-a?/c dialog%) (is-a?/c panel%) (is-a?/c pane%))
style :
(listof (one-of/c 'border 'control-border 'combo 'vscroll 'hscroll 'resize-corner 'gl 'no-autoclear 'transparent 'no-focus 'deleted)) = null
paint-callback : ((is-a?/c canvas%) (is-a?/c dc<%>) . -> . any) = void label : (or/c label-string? false/c) = #f gl-config : (or/c (is-a?/c gl-config%) false/c) = #f enabled : any/c = #t vert-margin : (integer-in 0 1000) = 0 horiz-margin : (integer-in 0 1000) = 0 min-width : (integer-in 0 10000) = graphical-minimum-width min-height : (integer-in 0 10000) = graphical-minimum-height stretchable-width : any/c = #t stretchable-height : any/c = #t The style argument indicates one or more of the following styles:
'border —
gives the canvas a thin border 'control-border —
gives the canvas a border that is like a text-field% control 'combo —
gives the canvas a combo button that is like a combo-field% control; this style is intended for use with 'control-border and not with 'hscroll or 'vscroll 'hscroll —
enables horizontal scrolling (initially visible but inactive) 'vscroll —
enables vertical scrolling (initially visible but inactive) 'resize-corner —
leaves room for a resize control at the canvas’s bottom right when only one scrollbar is visible 'gl —
obsolete (every canvas is an OpenGL context where supported) 'no-autoclear —
prevents automatic erasing of the background bitmap after calls to swap-bitmaps 'transparent —
ignored for an animated canvas 'no-focus —
prevents the canvas from accepting the keyboard focus when the canvas is clicked, or when the focus method is called 'deleted —
creates the canvas as initially hidden and without affecting parent’s geometry; the canvas can be made active later by calling parent’s add-child method The 'hscroll and 'vscroll styles create a canvas with an initially inactive scrollbar. The scrollbars are activated with either init-manual-scrollbars or init-auto-scrollbars, and they can be hidden and re-shown with show-scrollbars.
The paint-callback argument is ignored for an animated canvas.
The label argument names the canvas for get-label, but it is not displayed with the canvas.
The gl-config argument determines properties of an OpenGL context for this canvas, as obtained through the canvas’s drawing context. See also get-dc and get-gl-context in dc<%>.
Returns the device context of the background bitmap. This value changes across calls to swap-bitmaps.
method
(send an-animated-canvas swap-bitmaps) → any
Swaps the background and foreground bitmaps, displays the new foreground bitmap, and clears the new background bitmap (unless explicitly requested not to do so).
3 Examples"
3.1 Lines
This section contains an example animated graphics program that uses the animated-canvas% class to draw moving lines—
#lang racket/gui ; Lines animated canvas example. ; Draws moving line similar to those in the Qix video game. (require (planet williams/animated-canvas/animated-canvas)) (define-struct qix-segment (x1 y1 x2 y2)) (define-struct qix (x1 y1 x-dot1 y-dot1 x2 y2 x-dot2 y-dot2 color segments) #:mutable) (define (random-color) (make-object color% (random 256) (random 256) (random 256))) (define max-segments 12) (define (draw-qix the-qix) (define (draw-segment dc x1 y1 x2 y2 color) (send dc set-pen color 0 'solid) (send dc draw-line x1 y1 x2 y2)) (let ((dc (send canvas get-dc))) (for-each (lambda (qix) (for-each (lambda (segment) (draw-segment dc (qix-segment-x1 segment) (qix-segment-y1 segment) (qix-segment-x2 segment) (qix-segment-y2 segment) (qix-color qix))) (qix-segments qix))) the-qix) (send canvas swap-bitmaps))) (define (move-qix the-qix) (define (update-position-x x x-dot) (set! x (+ x x-dot)) (cond ((< x 0) (set! x (- x)) (set! x-dot (- x-dot))) ((> x (send canvas get-width)) (set! x (- (* 2 (send canvas get-width)) x)) (set! x-dot (- x-dot)))) (values x x-dot)) (define (update-position-y y y-dot) (set! y (+ y y-dot)) (cond ((< y 0) (set! y (- y)) (set! y-dot (- y-dot))) ((> y (send canvas get-height)) (set! y (- (* 2 (send canvas get-height)) y)) (set! y-dot (- y-dot)))) (values y y-dot)) (for-each (lambda (qix) ; Update the qix position (let-values (((x x-dot)(update-position-x (qix-x1 qix) (qix-x-dot1 qix)))) (set-qix-x1! qix x) (set-qix-x-dot1! qix x-dot)) (let-values (((y y-dot)(update-position-y (qix-y1 qix) (qix-y-dot1 qix)))) (set-qix-y1! qix y) (set-qix-y-dot1! qix y-dot)) (let-values (((x x-dot)(update-position-x (qix-x2 qix) (qix-x-dot2 qix)))) (set-qix-x2! qix x) (set-qix-x-dot2! qix x-dot)) (let-values (((y y-dot)(update-position-y (qix-y2 qix) (qix-y-dot2 qix)))) (set-qix-y2! qix y) (set-qix-y-dot2! qix y-dot)) ; Add a new segment to the segment list (set-qix-segments! qix (append (qix-segments qix) (list (make-qix-segment (qix-x1 qix) (qix-y1 qix) (qix-x2 qix) (qix-y2 qix))))) ; Remove old segments (when (> (length (qix-segments qix)) max-segments) (set-qix-segments! qix (cdr (qix-segments qix))))) the-qix)) (define break? #f) (define (main n-qix) (begin-busy-cursor) (send run-button enable #f) (set! break? #f) (let ((the-qix (let-values (((w h) (send canvas get-client-size))) (build-list n-qix (lambda (i) (make-qix (random w) (random h) (- (random 20) 10) (- (random 20) 10) (random w) (random h) (- (random 20) 10) (- (random 20) 10) (random-color) '())))))) (let loop () (let ((t (current-milliseconds))) (draw-qix the-qix) (move-qix the-qix) (sleep/yield (max 0.0 (/ (- 10.0 (- (current-milliseconds) t)) 1000.0))) (unless break? (loop))))) (send run-button enable #t) (end-busy-cursor)) ; GUI elements (define frame (instantiate frame% ("Animated Canvas Demo"))) (define panel (instantiate horizontal-panel% (frame) (alignment '(right center)) (stretchable-height #f))) (define run-button (instantiate button% ("Run" panel) (horiz-margin 4) (callback (lambda (b e) (main (send slider get-value)))))) (define stop (instantiate button% ("Stop" panel) (horiz-margin 4) (callback (lambda (b e) (set! break? #t))))) (define slider (instantiate slider% ("Number of qix" 1 100 frame) (init-value 10) (style '(horizontal)))) (define canvas (instantiate animated-canvas% (frame) (style '(border)) (min-width 800) (min-height 600))) (send frame show #t)
The following is a screen shot of the lines example.
3.2 Animated Histograms
This section contains an example animated graphics program that uses the animated-canvas% class to draw animated histograms.
|
superclass: vertical-panel% |
constructor
(new histogram-widget% [label label] [n n] [min-range min-range] [max-range max-range] [parent parent] [ [style style] [enabled enabled] [vert-margin vert-margin] [horiz-margin horiz-margin] [border border] [spacing spacing] [min-width min-width] [min-height min-height] [stretchable-width stretchable-width] [stretchable-height stretchable-height]]) → (is-a?/c histogram-widget%) label : string? n : exact-positive-integer? min-range : real? max-range : real?
parent :
(or/c (is-a?/c frame%) (is-a?/c dialog%) (is-a?/c panel%) (is-a?/c pane%))
style :
(listof (one-of/c 'border 'control-border 'combo 'vscroll 'hscroll 'resize-corner 'gl 'no-autoclear 'transparent 'no-focus 'deleted)) = null enabled : any/c = #t vert-margin : (integer-in 0 1000) = 0 horiz-margin : (integer-in 0 1000) = 0 border : (integer-in 0 10000) = 0 spacing : (integer-in 0 10000) = 0 min-width : (integer-in 0 10000) = graphical-minimum-width min-height : (integer-in 0 10000) = graphical-minimum-height stretchable-width : any/c = #t stretchable-height : any/c = #t The parent, style, enabled, vert-margin, horiz-margin, border, spacing, min-width, min-height, stretchable-width, and stretchable-height arguments are as described for vertical-panel.The label argument specifies a textual label for the histogram, the n argument specifies the number of bins in the histogram, and the min-range and max-range arguments specify the range of values for the histogram.
#lang racket/gui (require plot (planet williams/animated-canvas/animated-canvas) (planet williams/science/histogram)) (provide (all-defined-out)) (define histogram-widget% (class vertical-panel% ; Init parameters (init-field label) (init-field n) (init-field min-range) (init-field max-range) (init parent) (init (font normal-control-font)) ; Instantiate superclass (super-instantiate (parent)) ; Create graphical subelements (define message (instantiate message% (label this))) (define canvas (instantiate animated-canvas% (this) (style '(border)))) ; Recompute sizes and positions (send this reflow-container) ; Create histogram vector (define histogram (make-histogram-with-ranges-uniform n min-range max-range)) ; Draw histogram (define (draw-histogram (scale 1)) (let* ((dc (send canvas get-dc)) (width (send canvas get-width)) (height (send canvas get-height)) (n (histogram-n histogram)) (bins (histogram-bins histogram)) (ranges (histogram-ranges histogram)) (rects (for/list ((i (in-range n))) (let ((x0 (vector-ref ranges i)) (x1 (vector-ref ranges (+ i 1))) (y (vector-ref bins i))) (vector (make-ivl x0 x1) (make-ivl 0 y)))))) (plot/dc (rectangles rects) dc 0 0 width height #:x-min (vector-ref ranges 0) #:x-max (vector-ref ranges (- (vector-length ranges) 1)) #:x-label "x" #:y-min 0 #:y-max (histogram-max histogram) #:y-label "Count")) (send canvas swap-bitmaps)) ; Reset method (define/public (reset) (set! histogram (make-histogram-with-ranges-uniform n min-range max-range)) (draw-histogram)) ; Set value method (define/public (set-value value) (histogram-increment! histogram value) (draw-histogram))))
The main program, histogram-test.rkt, displays two animated histograms, one showing a unit Gaussian distribution and the other a triangular distribution.
#lang racket/gui (require (planet williams/science/random-distributions) "histogram-widget.rkt") (define (main n) (random-source-randomize! (current-random-source)) (for ((i (in-range n))) (let ((gaussian (random-unit-gaussian)) (tri (random-triangular 0.0 10.0 4.0))) (send histogram-1 set-value gaussian) (send histogram-2 set-value tri) (yield)))) (define frame (instantiate frame% ("Test Histogram Widget"))) (define histogram-1 (instantiate histogram-widget% ("Unit Gaussian" 40 -4.0 4.0 frame) (min-width 400) (min-height 200))) (define histogram-2 (instantiate histogram-widget% ("Triangular" 40 0.0 10.0 frame) (min-width 400) (min-height 200))) (send frame show #t) (main 10000)
The following is a screen shot of the histograms example.
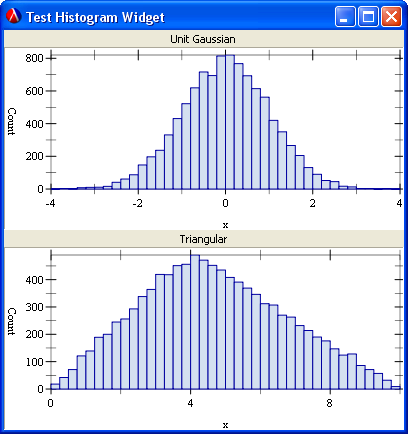
3.3 Animated 3D Plot
This section contains an example animated 3D plot for the plot collection.
#lang racket/gui (require plot (planet williams/animated-canvas/animated-canvas)) (define (main delta t-last) (parameterize ((plot3d-samples 21)) (let loop ((t 0.0)) (define (f x y) (* (sin (* 2.0 x)) (sin (* 2.0 y)) (cos t))) (when (<= t t-last) (let* ((dc (send canvas get-dc)) (width (send canvas get-width)) (height (send canvas get-height))) (plot3d/dc (contour-intervals3d f 0 pi 0 pi) dc 0 0 width height #:z-min -1 #:z-max 1) (send canvas swap-bitmaps) (loop (+ t delta))))))) (define frame (instantiate frame% ("Test Plot Animation"))) (define canvas (instantiate animated-canvas% (frame) (style '(border)) (min-width 400) (min-height 300))) (send frame show #t) (main (* 0.05 pi) 20.0)
The following is a screen shot of the 3D plot animation example.
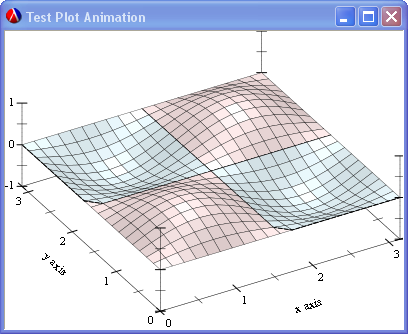
4 Issues and To Do
TBD